IMAGE GALLERY
Clinical Media Images
Early Detection of Ischemic Brain Injury using
Diffusion-Weighted Imaging (DWI)
Below are images generated as part of a comprehensive case study, in which we demonstrate the diagnostic value of the Embrace FSE-based DWI technique on four neonates admitted to the Shaare Zedek Medical Center NICU presenting clinical evidence of HIE.
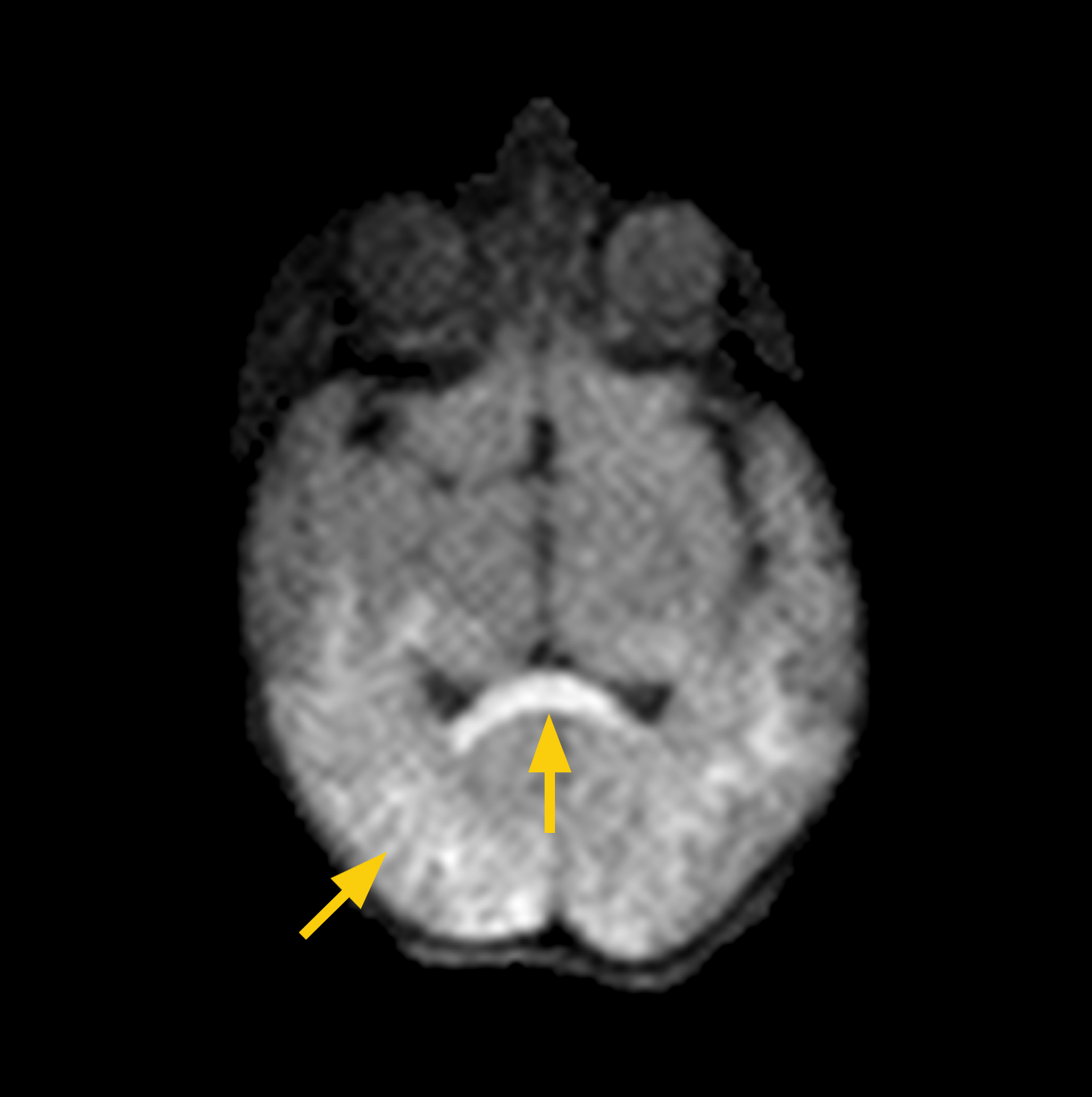
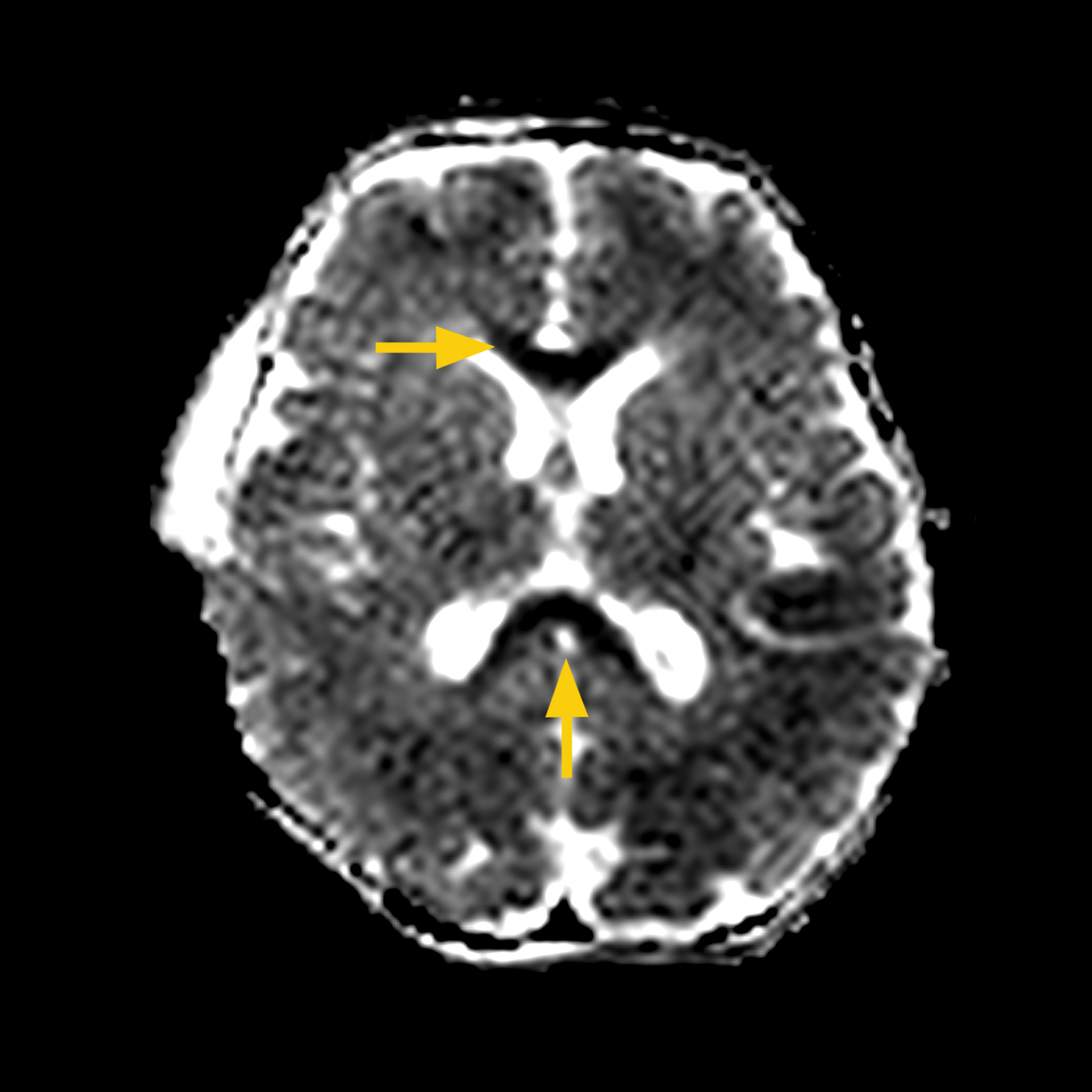
CASE 1:
HISTORY: Twin delivery at 37 weeks by STAT C-section for non-reassuring heart tones during labor. Apgar scores were 2/6/8 at 1/5/10 minutes. The aEEG showed an abnormal background pattern with seizures and the infant received therapeutic hypothermia for 72 hours. The clinical course was complicated by multi-system organ failure, hypotension treated with dopamine and hydrocortisone x 6 days. The MRI scan was completed on DOL 6.
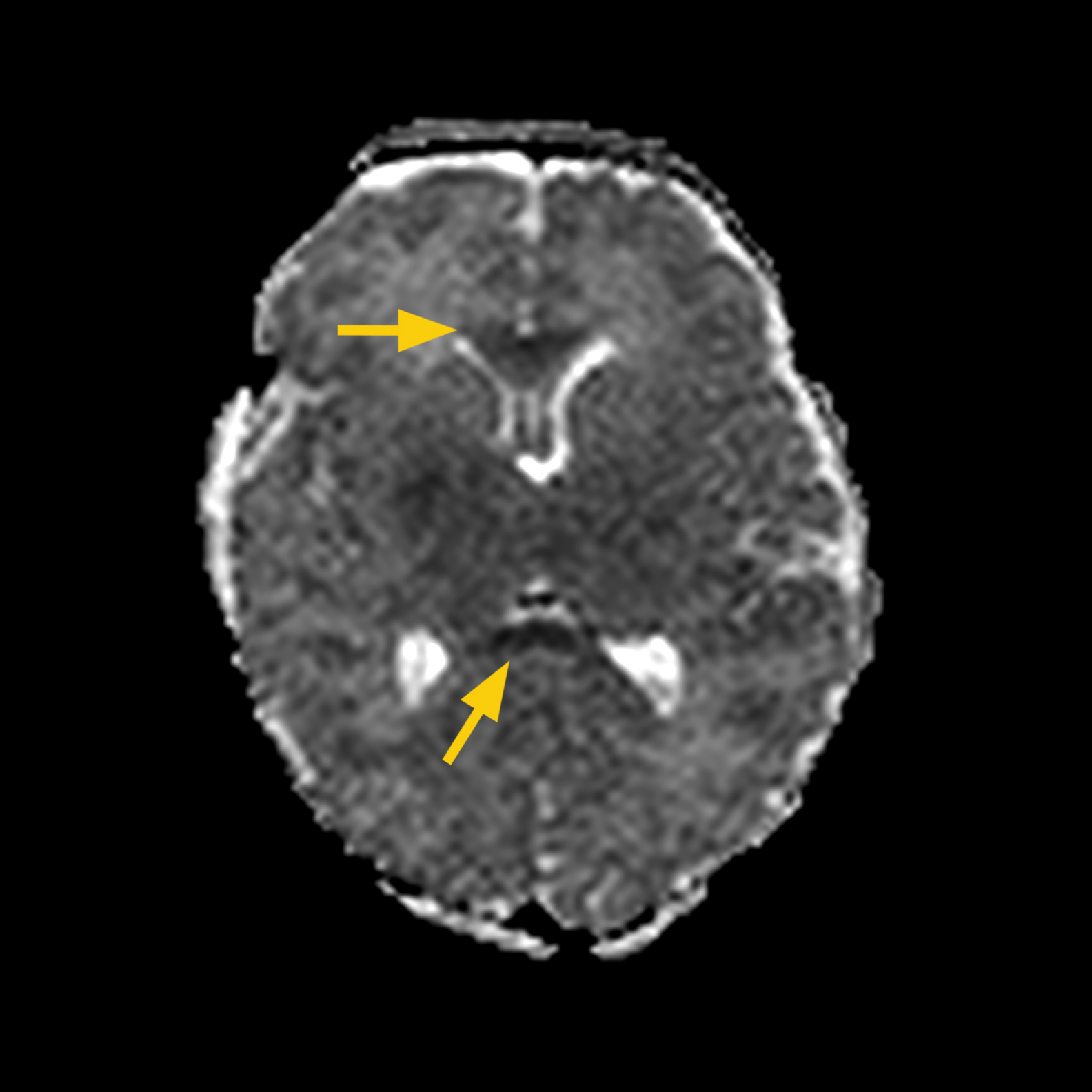
MRI FINDINGS: The DWI showed restricted diffusion in a posterior distribution and in the corpus callusum. Diffuse hypoxic ischemic injury (HIE) was diagnosed.
Images to the right show corpus callosum (arrow) and occipital lobe acute ischemia (arrow).
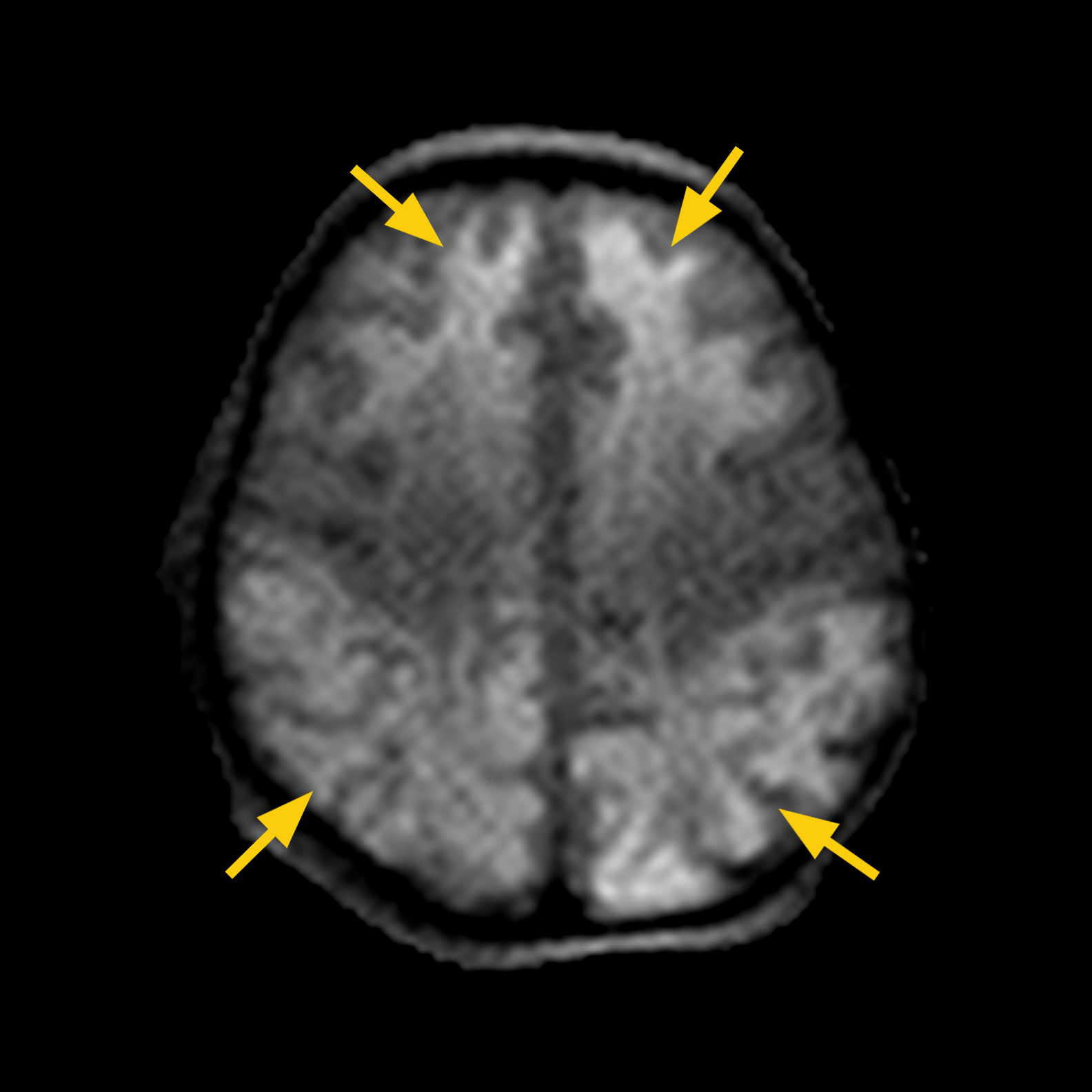
CASE 2:
HISTORY: Term infant born via emergency C-section, nuchal cord X 5 noted at delivery, and low Apgar scores. Infant received therapeutic hypothermia. MRI scan on DOL 6.
MRI FINDINGS: MRI scan showed diffuse restricted diffusion in anterior frontal lobes, bilateral parieto-occipital lobes and in corpus callosum.
Extensive ischemia in bilateral frontal and parietal-occipital lobes (a. or upper panel) and corpus callosum (b. or lower panel) are observed as hyper signal intensity in DWI Trace images (left) and hypo signal intensity in DWI ADC Map images (right).
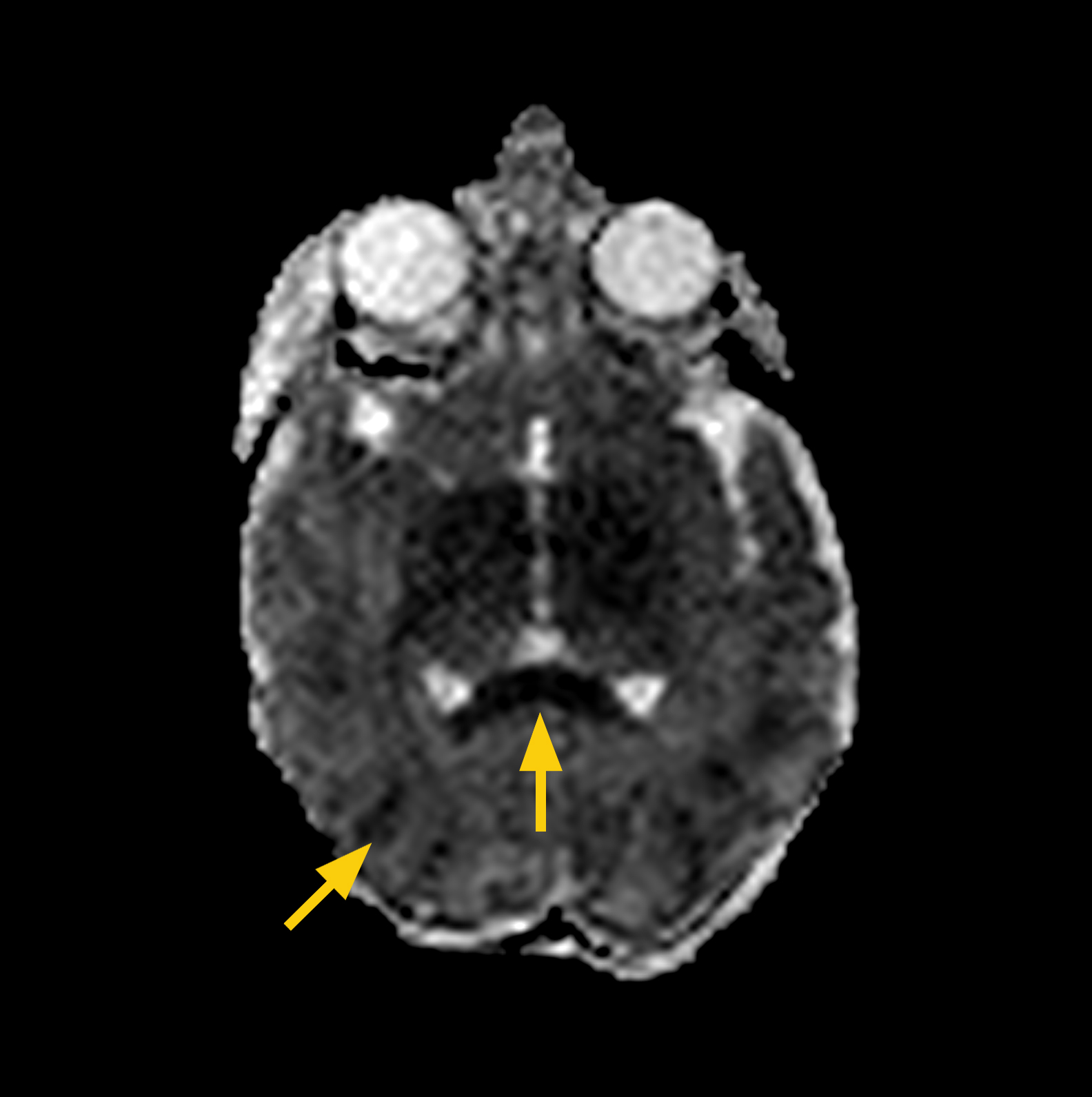
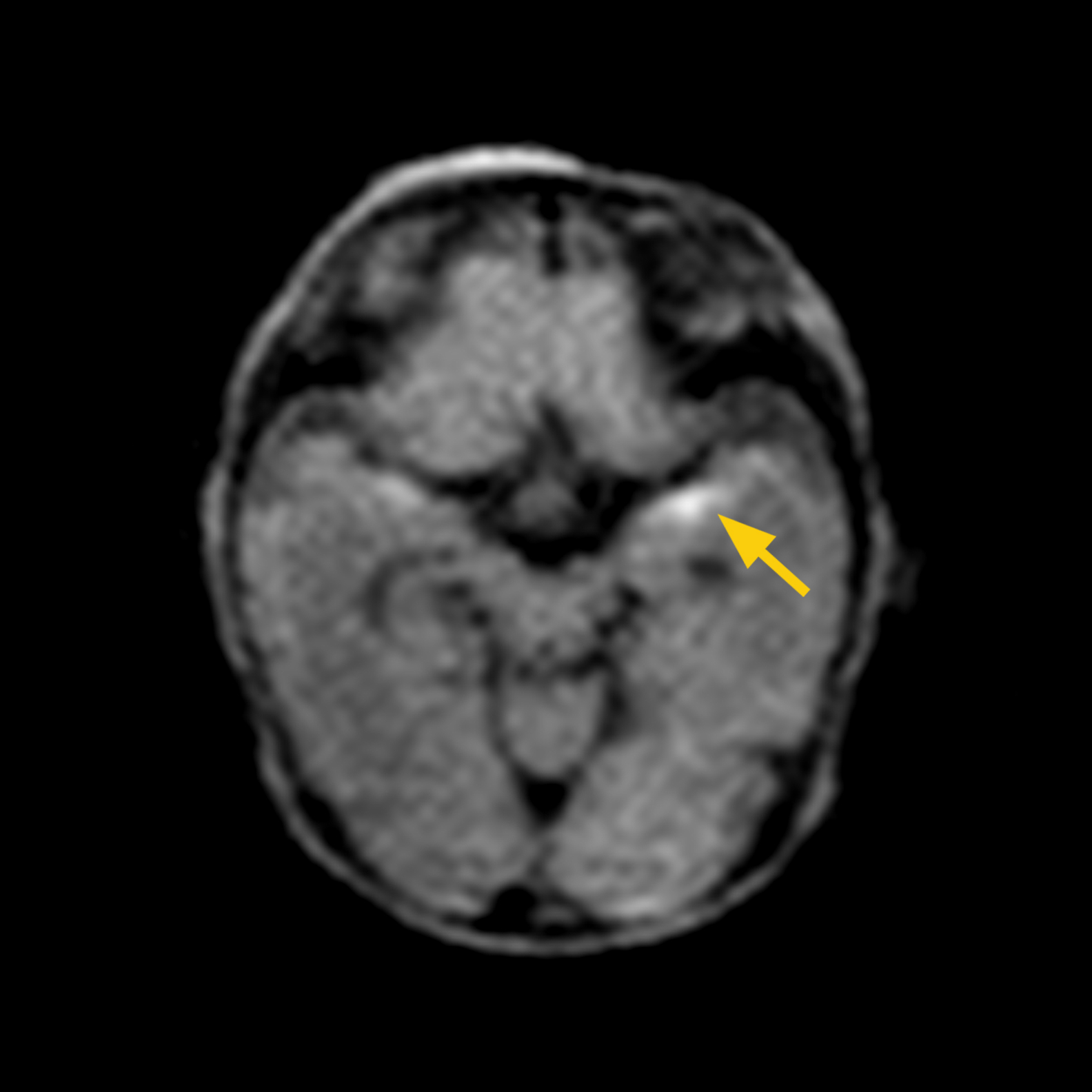
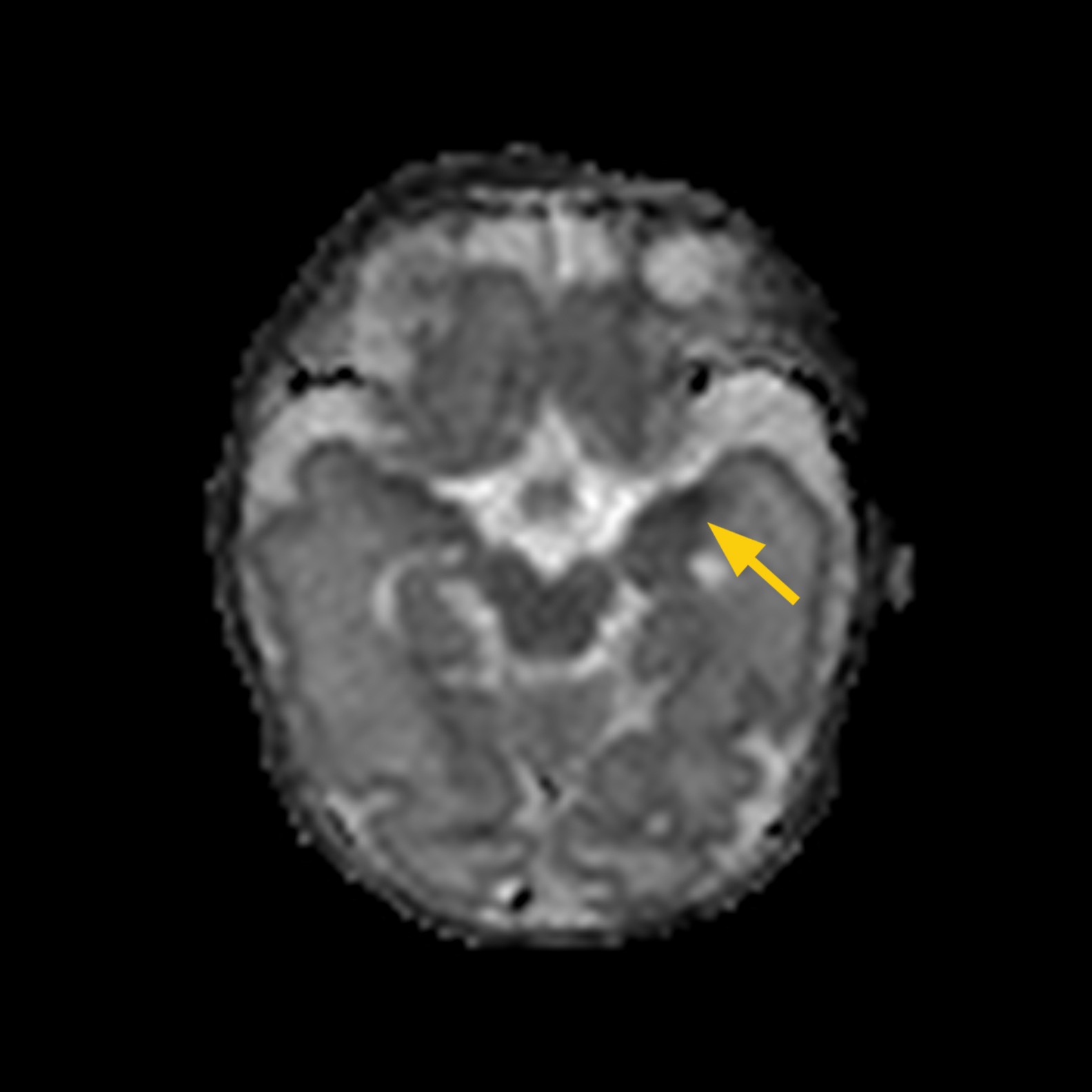
CASE 3:
HISTORY: Premature infant born at 30 weeks gestation. Infant presented with cardiac tamponade at 7 days old. MRI scan completed on DOL 12 (adjusted age 31 5/7 weeks..
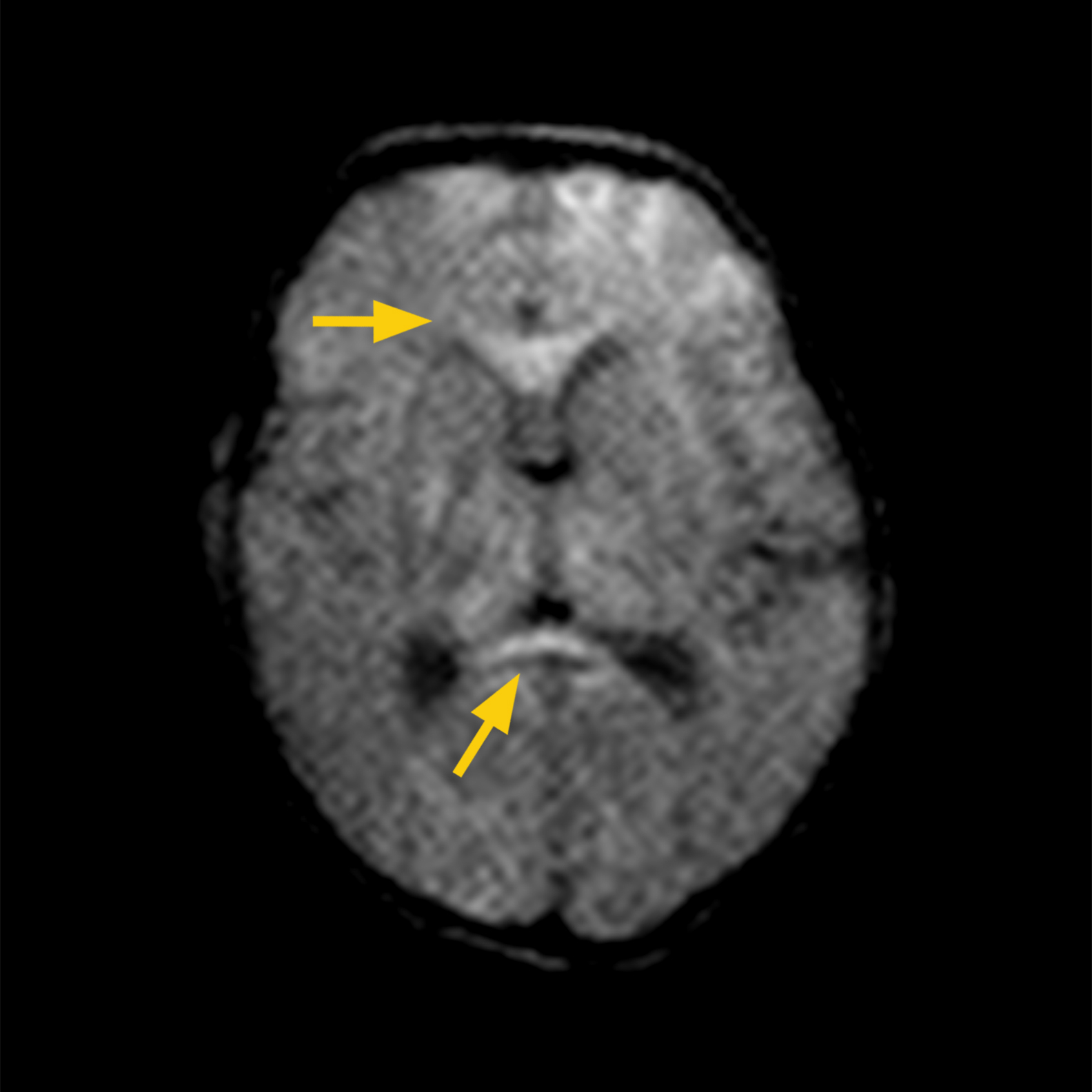
MRI FINDINGS: Restricted diffusion in left temporal lobe.
DWI shows left temporal lobe ischemia.
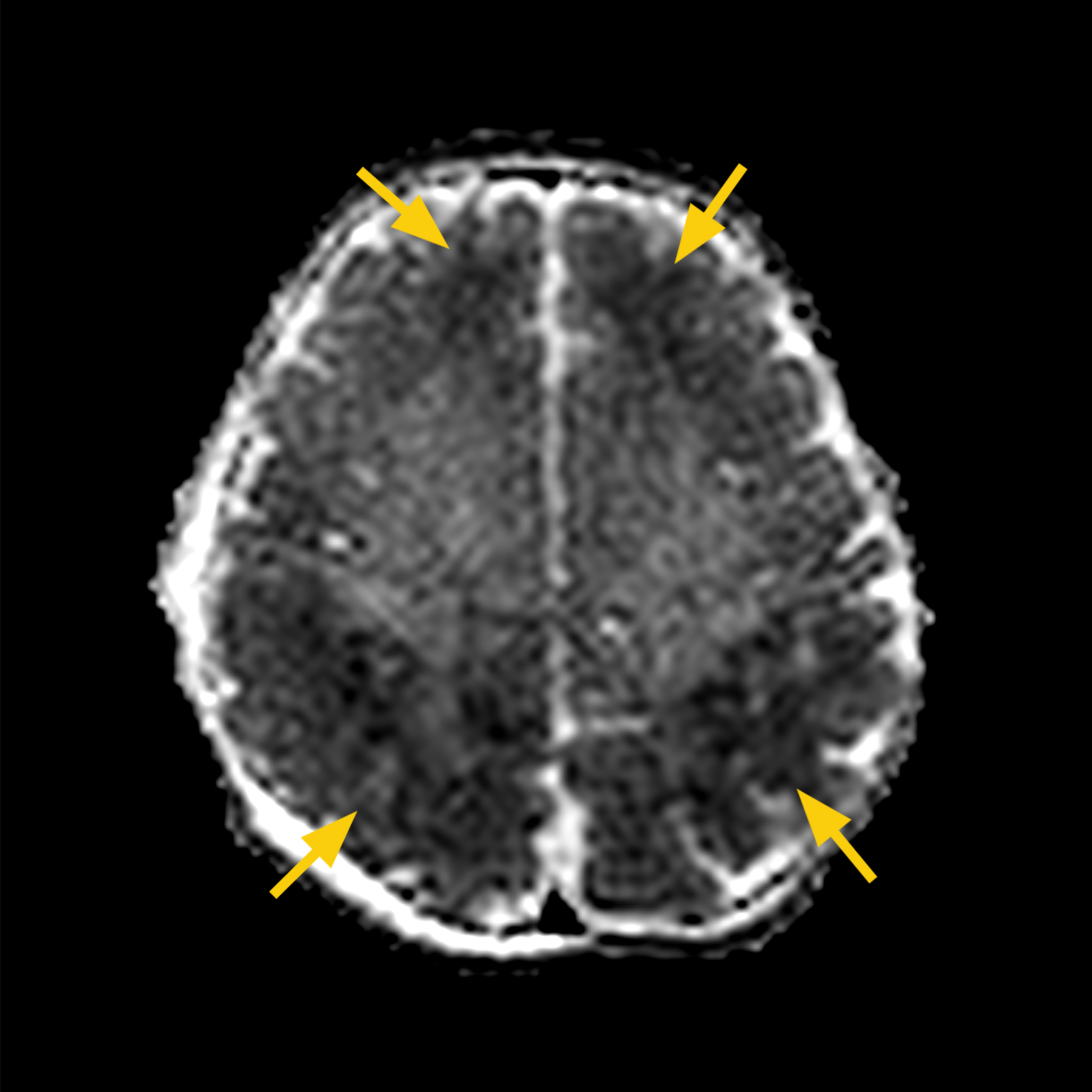
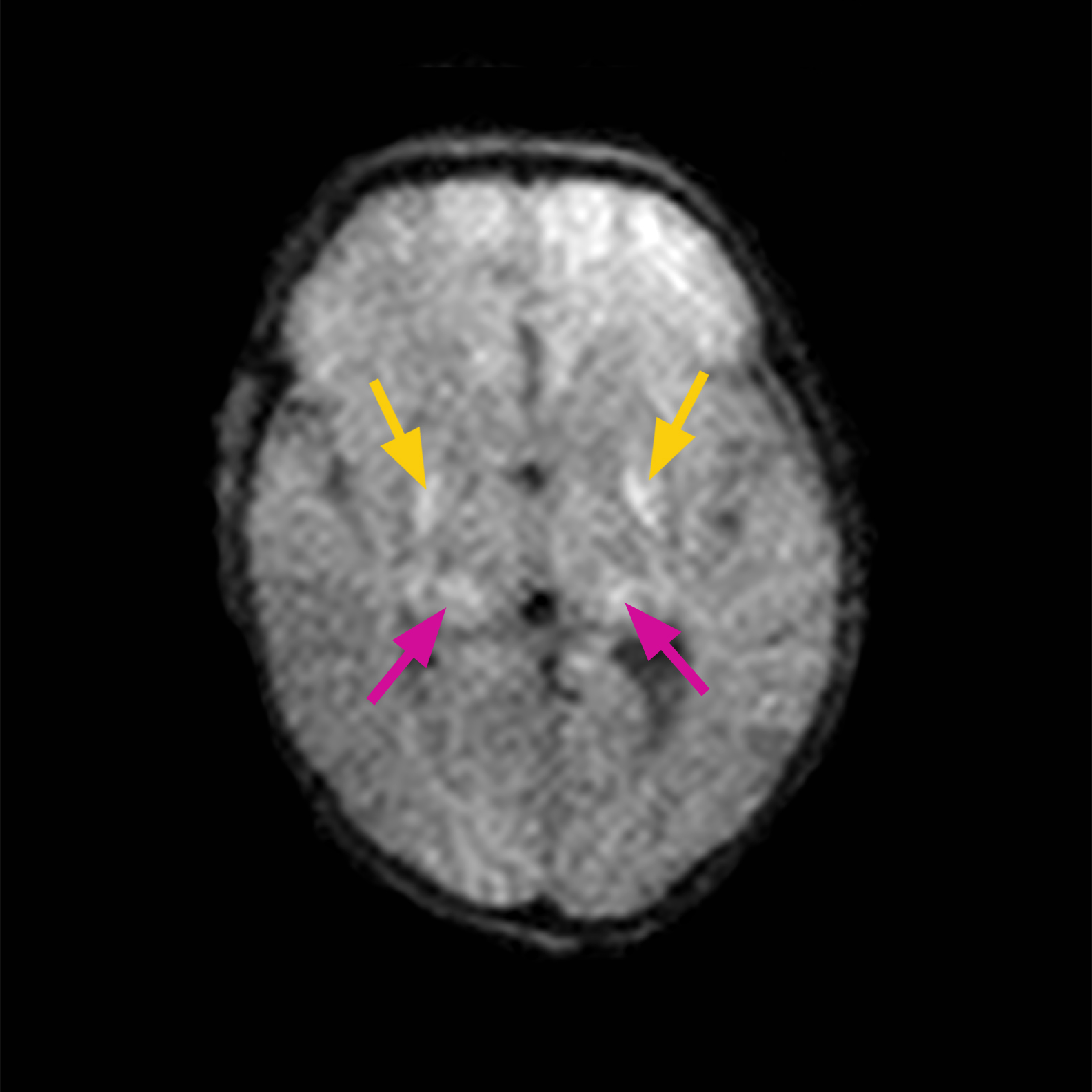
CASE 4:
HISTORY: Term infant with SGA, placental separation prior to delivery, received 40 minutes of CPR. Infant had seizures and received therapeutic hypothermia for 72 hours. MRI scan was completed on DOL 8.
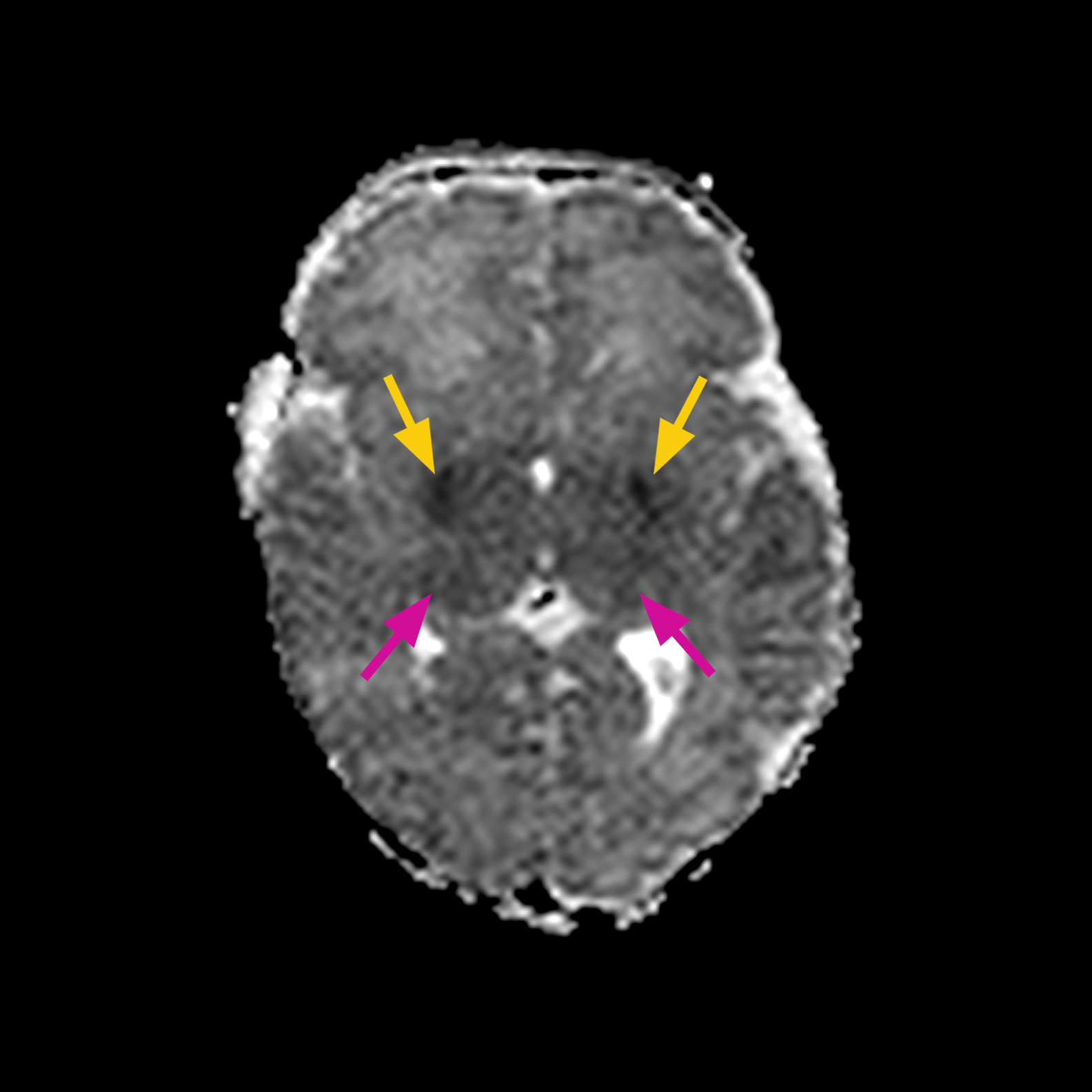
MRI FINDINGS: Bilateral restricted diffusion in globus pallidus, thalamus and corpus callosum.
DWI shows bilateral globus pallidus (yellow arrows), thalamus (red arrows) (a. or upper panel) and corpus callosum acute ischemia (b. or lower panel).
Early Detection of Ischemic Brain Injury using Diffusion-Weighted Imaging (DWI)
Neonatal hypoxi-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) occurs in 1.5 cases per 1,000 of all live births worldwide and is a devastating condition that may result in severe neurologic deficits or even death in children. Diagnostic imaging plays a critical role in the clinical assessment of suspected neonatal HIE. Click below to read the full case study.

About Aspect Imaging:
Aspect Imaging is a global leader in the design and development of compact, MR imaging systems for Pre-Clinical and Medical applications. Through state-of-the-art technology, Aspect Imaging offers innovative point-of-care MRI solutions, including the Embrace® Neonatal MRI System, which is designed to facilitate enhanced patient-centered diagnostic capabilities inside the NICU.
For more information, visit our website at www.aspectimaging.com.